EYE EXAMINATIONS
Eye examinations measurements to calculate the correct intraocular lens

Cataract is the clouding of the natural lens in our eye that may lead to blurring of vision. No-Blade Cataract Surgery, also known as Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (FLACS) uses a Femtosecond laser (a powerful light beam) to assist in removing the cataract. This technology gives more surgical precision and safety in cataract surgery.
The Z8 is the first mobile femtosecond laser for refractive and cataract surgery. This innovative laser provides a more powerful laser source allowing more flexibility without losing precision.

The most common type of intraocular lens has a monofocal optic with a single corrective power (focal point). Monofocal lenses are designed to provide clear vision for one distance, usually far, which is important for tasks such as driving. However, patients with monofocal IOLs may continue to need eyeglasses for activities at other distances, for example, reading.

Vision simulation with a monofocal lens: clear vision at distance
Similar to bifocal eyeglasses, bifocal intraocular lenses have two focal points to provide clear vision for both distance and up close. Patients treated with bifocal IOLs may need to wear eyeglasses for certain intermediaterange tasks (approx. 80 cm) such as computer work.

Vision simulation with a bifocal lens: clear near and distance vision
The most advanced intraocular lenses today, trifocal IOLs, have been used to successfully treat cataracts for several years. These lenses are designed to project multiple images onto the retina, which the brain combines into one sharp picture, allowing patients to see objects clearly at various distances – similar to progressive eyeglass lenses. Trifocal intraocular lenses are designed to enable not only clear far vision and a comfortable reading distance. This type of IOL provides in addition good intermediate vision, which is essential for performing daily activities such as cooking or computer work. As a result, many patients with trifocal lenses no longer need to wear glasses.
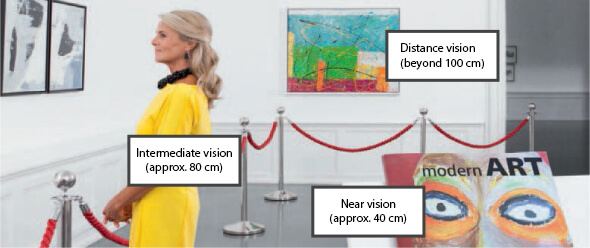
Vision simulation with a trifocal lens: clear near, intermediate and distance vision
Step 1: Corneal Incision
Starting with the corneal incision, the ophthalmologist (eye surgeon) uses a metallic blade to create the incision that allows access to the inside of the eye. When using femtosecond laser in this step we decrease the risk of inaccuracy, bleeding and inflammation allowing for a better healing process. With the help of 3D technology and the use of femtosecond laser, the surgeon can perform the incision with highest standards of accuracy. This allows the incision to self-heal and decrease the risk of inflammation and infection.
Step 2: Capsulotomy
Through the incision, the surgeon reach the clouded lens by opening the capsule that hold it in place. When using femtosecond laser in this step, we allow minimal damage to surrounding tissue! Because we need the remainder of the lens capsule to hold the artificial intraocular lens in place forever. Also the use of femtosecond laser in this step allows better stability positioning and centering of the IOL.
Step 3: Cataract Fragmentation!
Using femtosecond laser in this step (Femto-cataract) allows the surgeon to breaks up the cataract lens into smaller pieces. So less energy is used to remove it thus decreasing the risk for incision distortion!
Eye examinations measurements to calculate the correct intraocular lens
Same-day procedure with a local anesthetic such as eye drops
First day after surgery, then for approx. a month, as needed
Periodic check-ups by your eye doctor
Services offered : Eye Examination, Cataract surgery, Laser Vision Correction (LASIK), Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL), Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE), Management & Treatment of Eye Diseases Paediatric (Children) Eye Care, Corneal Reshaping Therapy (Ortho-K)